Describe the Structure of Phospholipid Bilayer
Liposomes are microscopic. This figure depicts the lipid bilayer and the structure of a phospholipid.
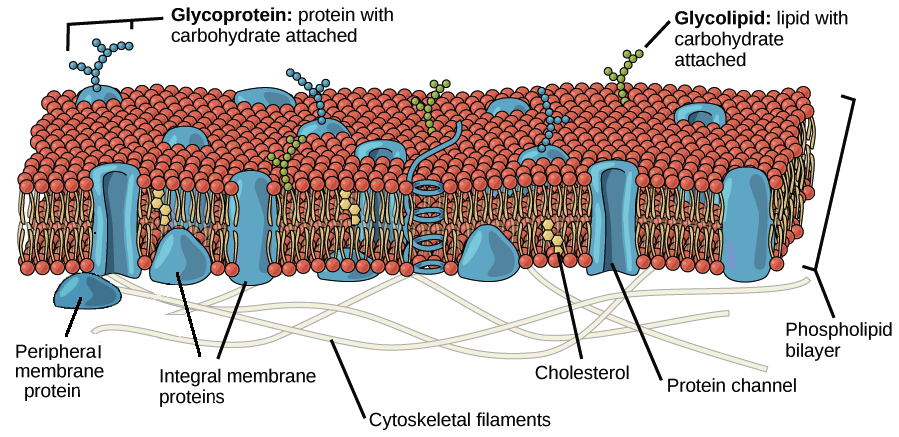
Structure Of The Plasma Membrane Article Khan Academy
D carbohydrates function as membrane channels.

. It is caused by the microorganism Giardia lamblia. This means that the experiments measure the partitioning of peptides between translocon channel and bilayer rather than between water-soluble and TM. Bacterial Classification Structure and Function Introduction The purpose of this lecture is to introduce you to terminology used in microbiology.
As discussed in the context of bacterial cell membranes the plasma membranes of eukaryotic cells may also adopt unique conformations. Lamblia can attach itself with its sucker. The plasma membrane is.
The hydrophilic components line up on the external and internal surface of. A phospholipid bilayer with various molecules embedded within and floating between the layers. The structure of the lipid bilayer allows only small non-polar substances such as oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass through the cell membrane down their concentration gradient by simple diffusion.
As membrane components phospholipids are selectively permeable also called semi-permeable meaning that only certain molecules can pass through them to enter or exit the cell. This bilayer membrane structure is also found in aggregate structures called liposomes. Lines below Hydrophobic tails.
Match each of the characteristics to the part of the lipid bilayer that has that property. Phospholipid bilayer as a versatile biological barrier. The drawing shows some of the structures present in G.
To see an enlarged segment of a phospholipid bilayer Click Here. Orange circles Hydrophilic heads. The phospholipids in the plasma membrane are arranged in two layers called aphospholipid bilayerAs shown in Figure below each phospholipid molecule has a head and two tailsThe head loves water hydrophilic and.
Each phospholipid molecule has. The reason is that the bi-layer looks like a mosaic and has a semi-fluid nature that allows lateral movement of proteins within the bilayer. Explain the processes of DNA replication including proofreading enzymes and translation in both.
E nonpolar ends of phospholipids are exposed to water inside and outside the cell. Discuss bacterial structure and the function of the different. The combined results indicate that an intact PmoC scaffold including Cu C and Cu D ligands supported by a hydrogen-bonding network and interior lipid bilayer is associated with enzymatic activity.
The phospholipid bilayer structure has both hydrophilic or water-loving and hydrophobic or water-fearing components. The eukaryotic plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and cholesterol embedded in it. For instance the plasma membrane of cells that in multicellular organisms specialize in absorption are often folded into fingerlike.
A Flagellum Sucker Nucleus Ribosomes Name one. In contrast to partitioning between bilayer interface and hydrocarbon core the translocon crystal structure suggests that hydrophobic peptides are released laterally from the protein-conducting channel into the membrane. The plasma membrane is composed mainly of phospholipids which consist of fatty acids and alcohol.
-a phospholipid bilayer with various molecules embedded within and floating between the layers. Describe how the structure of a cholera bacterium is different. Z describe the general importance of the cell molecules-water mineral ions carbohydrates lipids amino acids proteins nucleotides nucleic acids enzymes vitamins.
Membrane proteins are anchored in the phospholipid bilayer. This bilayer is formed by the amphiphilic phospholipids which have a hydrophilic preferring water phosphate head and a hydrophobic preferring to stay away from. L mark Giardiasis is an intestinal disease.
Molecules that dissolve in fat can pass through easily while molecules that dissolve in. The bipolar nature of this molecule is the key to how membranes work. Describe the different types of bacteria 3.
The phospholipid molecules can move about in their half the bilayer but there is a significant energy barrier preventing migration to the other side of the bilayer. Describe the structure and functional properties of eukaryotic cells with special attention to the mitochondria more generally how phospholipid bilayer membranes establish gradients and why that matters to function and how these functions are accomplished in Archaea 10. Explain how this is an adaptation to living in the intestines.
A Phospholipid Bilayer. The backbone structure of the cell membrane is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules called lipid bilayer or phospholipid bilayer. Cover different classification schemes for grouping bacteria especially the use of the Gram stain 2.
Hydrophobic Fatty acid chains repelled by polar molecules Heads. C protein molecules that perform important cellular functions float in a lipid bilayer. Z describe the structure and functions of plasma membrane cell wall endoplasmic reticulum ER cilia flagella nucleus ribosomes mitochondria chloroplasts golgi body peroxisome glyoxysome and lysosome.
Scientists Singer and Nicolson described the structure of the phospholipid bilayer as the Fluid Mosaic Model. These first structures of active pMMO obtained by embedding the enzyme in a native lipid bilayer provide critical insight into pMMO structure and function. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane Figure 316.
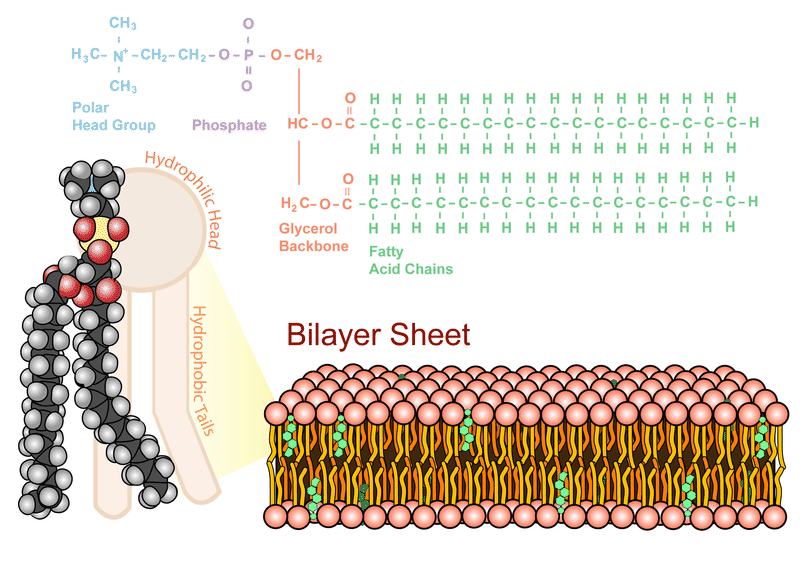
Phospholipid Bilayer Ck 12 Foundation

No comments for "Describe the Structure of Phospholipid Bilayer"
Post a Comment